Technology/Reliability
Technology/Reliability
CTM utilizes the latest flash and controller technology in a wide range of interfaces, form factors and capacities and has the technical expertise to identify the ideal solution for each application.
CTM’s advanced technology and manufacturing process controls result in highly reliable Memory Cards SSDs for customers with different needs.
Below are some major advanced technologies and reliabilities implemented in CTM Memory Cards and SSDs.
Memory Cards
High Reliability
CTM SD/SDHC/SDXC cards are with fortified gold-plating for harsh industrial applications, highest contact reliability, and minimum of 10,000 insertions.
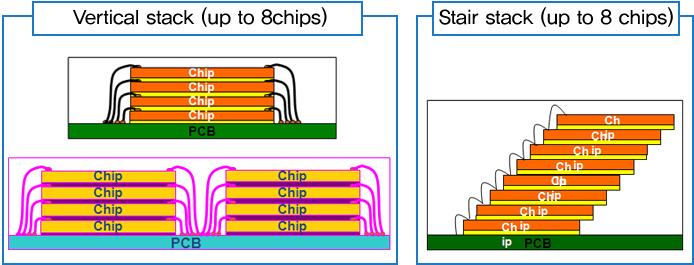
Multi Chip Stacking Technology up to 8-stack
:enables to maximize memory card density with 8-chip stack and offers different type of stacking solutions
Memory Card Test Process
Every single piece of CTM SD/SDHC/SDXC card is tested by three procedure to keep utmost high reliability level.
-
1 Controller Test
Assembly Check, save ISP, Format, and CID monitoring. -
2 Maverick Test
1) Check ISP code
2) Assembly Check
3) Check standby currentTEST ITEM UNIT DC test Input Leakage low nA Spec : -10 ~ 10 uA Input Leakage High nA Spec : -10 ~ 10 uA AC test IDD Standby Current Write current uA Max : 1000uA
Max : 50mAFunction Read/Write -
3 IMI Test
Card performance check : Write Multiple block / Read Multiple block
CTM SD/SDHC/SDXC cards are passed for minimum 3,000 cycles of sudden power failure.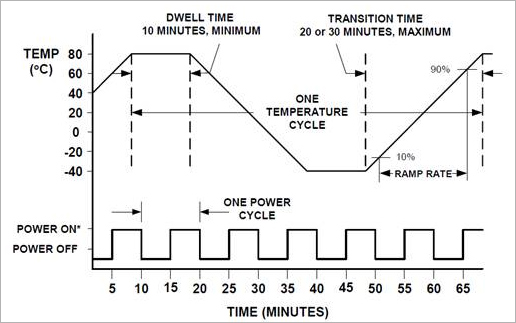
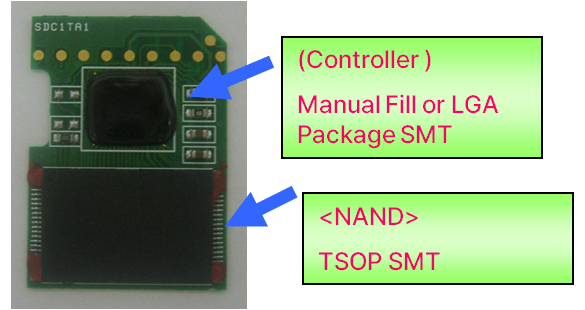
COB vs. SMT Type SD Card Comparison
COB : Chip On Board (Using Wafer level semiconductor assembly process)
SMT : Surface Mount Technology (Using Soldering process)
COB type

- High reliability against bending.
- Waterproof
- Dust proof
- High reliability against shock and vibration
- High Security (Cannot open NAND area)
SMT type
- Weak from mechanical damage
- Not waterproof
- Low protection against dust
- Low protection against shock and vibration
- Low protection against security

SSDs
Sudden Power Off Recovery (SPOR)
Power management at the solid state drive level is critical to prevent data corruption due to unexpected power loss.
When programming a NAND flash page, the program operation must complete to ensure the data is stored reliably within the page. Data is at risk if flash memory cells are in the process of being programmed when power to the drive is lost. The risk is compounded for MLC NAND flash memory, which uses the same physical page of memory cells to store two logical pages of data.
The Sudden Power Off Recovery (SPOR) is a scheme to protect data from lost during a sudden power off when SSD is under writing.
CTM utilizes both hardware or software design to prevent data corruption when there is a power failure.
Quick Erase
CTM technology provides the encryption function which is implemented by the hardware AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). Compared to the software encryption, hardware encryption presents better performance in data protection and processing. By the hardware AES encryption, the data will be encrypted before it is written into flash memory. After the encrypted data is written into flash memory, the data cannot be read.
CTM technology provides two methods to fast erase data: by software or by hardware. As for software method, users can activate the function of fast erasing with specific software commands. As for hardware method, CTM provides a switch to activate the function of fast erasing.
Trim
The TRIM feature works by actively deleting invalid data from the blocks, which helps to maintain the write performance at its full potential. As a block must be erased before it can be reprogrammed, TRIM improves write performance by proactively erasing blocks that contain invalid data. This allows the SSD to write new data without first having to perform a time-consuming erase command.
S.M.A.R.T
S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) is a feature set defined by the ANSI ATA Specifications. The feature set consists of a set of commands which allow the host to retrieve information about the storage device’s health status.
This allows the user to know in advance impending device failures and act accordingly before the device actually fails.
Through the S.M.A.R.T system, CTM SSDs incorporates suites of advances diagnostics that monitor the internal operation of the drive and provide an early warning for many types of potential problems. S.M.A.R.T monitors SSD performance, detects faulty sectors, perform recalibration and CRC error correction. When a potential problem is detected, the SSD can be repaired or replaced.
Wear Leveling Technology
NAND flash has individually erasable blocks, each of which can be put through a finite number of erase cycles before becoming unreliable. That is, after a specific number of cycles for each block, the error rate can significantly increase.
Unfortunately, in most cases, the flash media is not used evenly. In certain areas, such as for the file system, the data is updated more frequently than for other areas, and will wear out sooner in those areas.
Wear leveling mitigates this issue by arranging data so that erasures and re-writes are distributed evenly across the entire device. Thus, no single sector prematurely fails due to a high concentration of program/erase cycles.
CTM uses an advanced wear leveling algorithm, which can efficiently spread usage throughout the entire flash media area. By implementing both dynamic and static wear leveling algorithms, the life expectancy of the flash media can be improved significantly.
NCQ Technology
NCQ stands for Native Command Queuing technology. NCQ technology allows the drive to manage multiple outstanding commands more efficiently, which significantly increases concurrent access capability.
It solves the concurrent access bottleneck associated with traditional HDDs in some high concurrent access applications such as on-line banking, on-line ticketing and VOD.
As part of the latest Serial ATA specification, NCQ requires an NCQ-capable SSD and either a motherboard or a PCI adapter card with NCQ support. NCQ technology is incorporated into select SSDs from CTM.
Bad Block Management
Bad blocks are blocks that contain one or more bits for which the reliability is not guaranteed. Bad blocks can occur when the flash is shipped or can develop during the usage.
CTM implements an efficient bad block management algorithm into the solid state hard drive to detect factory produced bad blocks as well as those that develop over the lifetime of the device. This process is completely transparent to the user through the use of S.M.A.R.T. command tools, i.e., the user will not be aware of the existence of the bad blocks during operation.
Write Protection
If the write protect is activated, the data stored in flash memory will remain in the read-only mode. At this mode, users can only read data but not write any data into flash memory.
CTM provides two methods to implement write protect: by software or by hardware. As for software method, users can activate or disable the function of write protect with specific software commands. As for hardware method, CTM provides a switch to activate or disable the function of write protect.